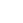- Synonyms
- Sak42D
- Source
- Escherichia coli.
- Molecular Weight
- Approximately 15.6 kDa, a single non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 136 amino acids.
- Size
- 100µg/ 500µg/ 1mg
- AA Sequence
- SSSFDKGKYK KGDDASYFEP TGPYLMVNVT GVDGKRNELL SPRYVEFPIK PGTTLTKEKI EYYVEWALDA TAYKEFRVVE LDPSAKIEVT YYDKNKKKEE TKSFPITEKG FVVPDLSEHI KNPGFNLITK VVIEKK
- Purity
- > 97% by SDS-PAGE and HPLC analyses.
- Biological Activity
- Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The specific activity determined by fibrining lysis in agarose plate is 5.0 × 104 IU/mg.
- Physical Appearance
- Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder.
- Formulation
- Lyophilized from a 0.2 µm filtered concentrated solution in PBS, pH7.0, 0.02 % Tween80.
- Endotoxin
- Less than 1 EU/µg of rSAK as determined by LAL method.
- Reconstitution
- We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Reconstitute in sterile distilled water or aqueous buffer containing 0.1 % BSA to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/mL. Stock solutions should be apportioned into working aliquots and stored at ≤ -20 °C. Further dilutions should be made in appropriate buffered solutions.
- Stability & Storage
- Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 3 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- Usage
- This material is offered by Shanghai PrimeGene Bio-Tech for research, laboratory or further evaluation purposes. NOT FOR HUMAN USE.
- SDS-PAGE
- Reference
- 1. Matsuo O, Okada K, Fukao H, et al. 1990. Blood, 76: 925-9.
2. Collen D, Schlott B, Engelborghs Y, et al. 1993. J Biol Chem, 268: 8284-9.
3. Shishido Y, Matsumoto T, Sakai M, et al. 1994. Biol Pharm Bull, 17: 1060-4.
4. Ohlenschlager O, Ramachandran R, Flemming J, et al. 1997. J Biomol NMR, 9: 273-86.
- Background
- Staphylokinase is an amino acid enzyme secreted by several species of streptococci. It is a 16kDa potent plasminogen activator that converts plasminogen into plasmin which can digest fibrin the major constituent of blood thrombi. SAK forms 1:1 complex with plasmin, which is a positive feedback of producing other complexes. Recent studies on the thrombolytic potential of recombinant SAK in achieving early perfusion in myocardial infarction and in the dissolution of platelet-rich clot have clearly established its immense utility in clinical medicine as a thrombolytic agent and suggested that it can be developed as a potent clot-dissolving agent.









 COA Application
COA Application