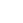- Synonyms
- Kabikinase, Streptase, Kinalysin, Plasminokinase, SK
- Source
- Escherichia coli.
- Molecular Weight
- Approximately 47.3 kDa, a single non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 414 amino acids.
- Size
- 100µg/ 500µg/ 1mg
- AA Sequence
- IAGPEWLLDR PSVNNSQLVV SVAGTVEGTN QDISLKFFEI DLTSRPAHGG KTEQGLSPKS KLFATDSGAM PHKLEKADLL KAIQEQLIAN VHSNDDYFEV IDFASDATIT DRNGKVYFAD KDGSVTLPIQ PVQEFLLKGH VRVRPYKEKP VQNQAKSVDV EYTVQFTPLN PDDDFRPALK DTKLLKTLAI GDTITSQELL AQAQSILNKN HPGYTIYERD SSIVTHDNDI FRTILPMDQE FTYHVKNREQ AYRINKKSGL NEEINNTDLI SEKYYVLKKG EKPYDPFDRS HLKLFTIKYV DVNTNELLKS EQLLTASERN LDFRDLYDPR DKAKLLYNNL DAFGIMDYTL TGKVEDNHDD TNRIITVYMG KRPEGENASY HLAYDKDRYT EEEREVYSYL RYTGTPIPDN PNDK
- Purity
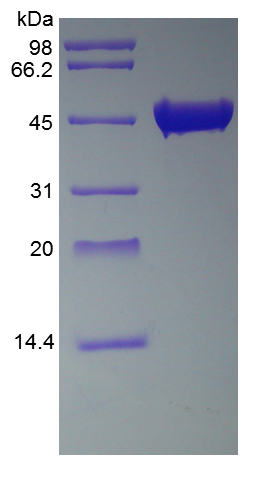
- > 97 % by SDS-PAGE and HPLC analyses.
- Biological Activity
- Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The specific activity determined by fibrining lysis in agarose plate is 8.0 × 104 IU/mg.
- Physical Appearance
- Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder.
- Formulation
- Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered concentrated solution in PBS, pH 7.4, 0.02% Tween20.
- Endotoxin
- Less than 1 EU/μg of rSK as determined by LAL method.
- Reconstitution
- We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Reconstitute in sterile distilled water or aqueous buffer containing 0.1 % BSA to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Stock solutions should be apportioned into working aliquots and stored at ≤ -20 °C. Further dilutions should be made in appropriate buffered solutions.
- Stability & Storage
- Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 3 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- Usage
- This material is offered by Shanghai PrimeGene Bio-Tech for research, laboratory or further evaluation purposes. NOT FOR HUMAN USE.
- SDS-PAGE
- Reference
- 1. Lorch H, Zwaan M, Siemens HJ, et al. 2000. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 23: 273-8.
2. Khan N, Mian I, Javed A, et al. 2003. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad, 15: 20-2.
3. Couto LT, Donato JL, de Nucci G. 2004. Braz J Med Biol Res, 37: 1889-94.
4. Armstrong PW. 2010. Nat Rev Cardiol, 7: 67-9.
- Background
- Streptokinase is a thrombolytic agent i.e. it dissolves vascular thrombi. This potent agent is derived from the beta haemolytic streptococci and is consequently associated with the risk of anaphylaxis. Streptokinase acts by stimulating the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin. It’s a proteolytic enzyme which is able to disrupt fibrin stability and production.









 COA Application
COA Application