- Synonyms
- B-cell differentiation factor I, Eosinophil differentiation factor, TRF
- Source
- Escherichia coli.
- Molecular Weight
- Approximately 26.5 kDa, a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein containing two 116 amino acids.
- AA Sequence
- MIPTEIPTSA LVKETLALLS THRTLLIANE TLRIPVPVHK NHQLCTEEIF QGIGTLESQT VQGGTVERLF KNLSLIKKYI DGQKKKCGEE RRRVNQFLDY LQEFLGVMNT EWIIES
- Purity
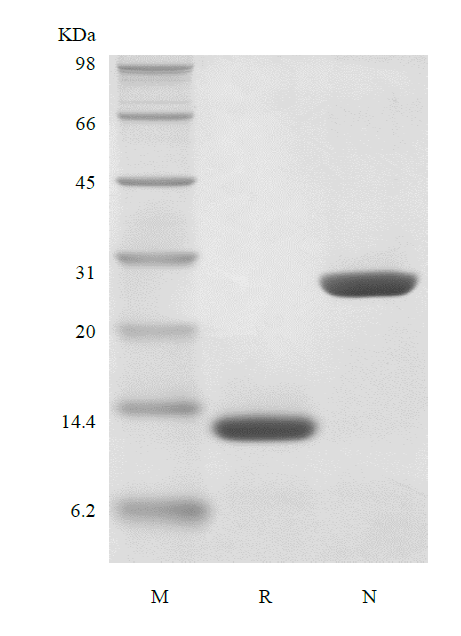
- > 98 % by SDS-PAGE and HPLC analyses.
- Biological Activity
- Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The ED50 as determined by a cell proliferation assay using human TF-1 cells is less than 0.1 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of > 1.0 × 107 IU/mg.
- Physical Appearance
- Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder.
- Formulation
- Lyophilized from a 0.2 µm filtered concentrated solution in 20mM PB, pH 7.5, 3 % trehalose, 0.1 % Tween-80.
- Endotoxin
- Less than 1 EU/µg of rHuIL-5 as determined by LAL method.
- Reconstitution
- We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Reconstitute in sterile distilled water or aqueous buffer containing 0.1 % BSA to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Stock solutions should be apportioned into working aliquots and stored at ≤ -20 °C. Further dilutions should be made in appropriate buffered solutions.
- Stability & Storage
- Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 3 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- Usage
- This material is offered by Shanghai PrimeGene Bio-Tech for research, laboratory or further evaluation purposes. NOT FOR HUMAN USE.
- SDS-PAGE
- Reference
- 1. MV Milburn, AM Hassell, MH Lambert, et al. 1993. Nature, 363: 172-6.
2. JS Lee, HD Campbell, CA Kozak, et al. 1989. Somat Cell Mol Genet, 15: 143-52.
3. BH van Leeuwen, ME Martinson, GC Webb, et al. 1989. Blood, 73: 1142-8.
4. S Dubucquoi, P Desreumaux, A Janin, et al. 1994. J Exp Med, 179: 703-8.
- Background
- The IL-5 gene is located on chromosome 5 in humans, in close proximity to the genes encoding IL-3, IL-4, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), which are often co-expressed in TH2 cells. Through binding to the IL-5 receptor, IL-5 stimulates B cell growth and increases immunroglobulin secretion. It is also a key mediator in eosinophil activation. Interleukin-5 has long been associated with the cause of several allergic diseases including allergic rhinitis and asthma. IL-5 is a 115-amino acid (in human, 133 in the mouse) -long TH2 cytokine that is part of the hematopoietic family. Unlike other members of this cytokine family (namely IL-3 and GM-CSF), this glycoprotein in its active form is a homodimer.









 COA Application
COA Application